Cricket: ODI, Test, T20I, Worldcup Winner List, Related all Topics.
Cricket:- Cricket is the most loved game in the world, played between two teams of eleven players. It is a bat-and-ball game played on a grass field. The game is played over several innings, with each team taking turns batting and bowling. The team scoring the most runs in each inning wins the match. Cricket is an English word in itself. Cricket is called “Golgattam Lakad Pattam De Danadan Competition” in Hindi.
History:-
Cricket, initially known as the national summer game of England, has gained immense popularity around the world. The popularity is such that it is not limited to the professional field only; rather, people of all ages and genders are seen playing cricket in their streets and places. This article explains the basic rules of the game. It provides information about cricket pitches and important rules used during the game. It also features a discussion of some important terminology and legends of the game.
No one has yet presented any concrete evidence about when and how the game of cricket originated. The origin of cricket is not documented, and no one has presented any specific evidence about it. Is. However, there is a dominant belief that cricket probably originated in England, which is supported by various books and documents. England played an important role in introducing and spreading cricket globally. The formation of the Hambledon Club in 1760, later transformed into the Marylebone Cricket Club (MCC), is considered significant in the history of cricket. The specific details of cricket’s origins are uncertain, but England’s influence has been significant, ushering in an important era in the development of the game. England is called the birthplace of cricket. The national game of England is also cricket. Cricket started in England in the year 1611, in the 70th century. Cricket is a team sport played outdoors. Cricket originated in England and gradually became popular throughout the world.
Cricket Once upon a time, cricket was a foreign game, but from there it reached the developed and developing countries of the world. The establishment of the Imperial Cricket Club in 1909 was an important step that marked the beginning of the tradition of playing cricket not only in England but across the world, but it also helped elevate cricket to the heights of excellence on the international stage. The Imperial Cricket Club, established in 1909, was renamed the International Cricket Conference in 1956. The introduction of cricket to India was facilitated by the British government, and the match between England and Australia in 1877 was the first official cricket match. The most official organization of cricket is MCC. also originated in England and gradually its influence spread worldwide, and cricket boards of all countries started working under it.
Audience:-
This article is for those who want to know and learn about cricket. It is prepared keeping in mind that the reader is unaware of the basics of the game. It is a basic guide to help a beginner understand the game of cricket. Before proceeding with this article, you are required to have a passion for cricket and an eagerness to acquire knowledge on the same. The information given here is to enhance your knowledge about the game. However, there is no comprehensive guide on how to play it. But after knowing all the rules of cricket, people will become more interested in it.
Objective:-
Cricket is indeed an outdoor game that is played on the ground. The main objective of the game is to score more runs than the opposing team. This is achieved by attempting to score as many runs as possible while also trying to restrict the other team’s score and dismissing their batsmen. If you are interested in learning more about the game, its popular terms, and its rules, I suggest you read further in the document.
Team Size:-
In cricket, each playing team consists of 11 players, and a captain is appointed among them. Apart from these 11 players, each side has a few more players who can only take the field as a replacement for an injured team member. But that player can only field; there should be 11 players on the fielding team, and the opposition team can send only two batsmen on the field at the time of play.
For all international tournaments organized by the International Cricket Council (ICC), the governing body of cricket, it is necessary to have a team of 15 members, or along with this, as per the recent ICC rules, you may survive in this competition with 18 members.
Asian countries participating in cricket:-
Cricket originated in England and gradually became popular all over the world. Gradually, this game gained popularity on the Asian continent as well. India, Pakistan, Sri Lanka, and Bangladesh also started playing this game.
Asian Cricket Council
The Asian Cricket Council was established in 1983 and included all the cricket-playing countries in Asia. It was formed to develop the Asian Cricket Council and cricket in Asia.
In the late 1900s, Asian countries like India, Sri Lanka, and Pakistan made their mark on world cricket by each winning the World Cup once. This led to the formation of the Asian Cricket Conference in 1983, which took charge of the development of the game in the rest of Asia. By the 21st century (2003–2014), Bangladesh had become a new force in Asian cricket. The Asian Cricket Conference was renamed the Asian Cricket Council in 2003, headquartered in Kuala Lumpur. The council is subordinate to the ICC and has an association of 25 countries.
Cricket-playing countries in Asia
| Country | Membership Status |
|---|---|
| Afghanistan | Associate member (ODI status) |
| Bahrain | Affiliate Member |
| Bangladesh | Full Member |
| Bhutan | Affiliate Member |
| Brunei | Former associate member (2002–2015) |
| Cambodia | Unavailable |
| China | Affiliate Member |
| Hong Kong | Associate member (ODI status) |
| India | Full Member |
| Iran | Former associate member (left establishment) |
| Kuwait | Associate Member |
| Malaysia | Associate member |
| Maldives | Affiliate Member |
| Myanmar | Associate Member |
| Nepal | Former Associate Member (left the establishment) |
| Oman | Associate member (T20 status) |
| Pakistan | Full Member |
| Qatar | Affiliate Member |
| Saudi Arabia | Associate Member |
| Singapore | Associate Member |
| Sri Lanka | Full Member |
| Chinese Taipei | Unavailable |
| Tajikistan | Unavailable |
| Thailand | Associate member |
| United Arab Emirates | Associate member (ODI status) |
Non-Asian Countries Participating in Cricket:-
Cricket’s roots in England, Australia, the West Indies, and South Africa date back to the early 20th century. Abe Bailey, then President of the South Africa Cricket Association, conceived the idea of an international council, leading to the formation of the Imperial Cricket Conference in 1906, later known as the International Cricket Council (ICC). Over the past two decades, Zimbabwe, Kenya, Ireland, the Netherlands, Canada, Scotland, and the UAE have joined global tournaments. The game has expanded to over 100 countries, including recent adoption by the United States. International cricket features three formats: test matches (5 days), one-day internationals (50 overs), and T-20 internationals (20 overs), with T-20 emerging as the most popular format in the last five years. Explore this dynamic global sport governed by the ICC. T-20 is the latest and most popular format over the last five years.
What is Test Match, Types, it’s All Rules:-
Test match:– Test cricket is a form of first-class cricket played at the international level between teams representing full member countries of the International Cricket Council (ICC). Test cricket is a format of cricket in which the longest duration of the match is five days. Each day’s play in a test match usually lasts for seven hours. This is considered the highest standard of the game. This is the real test of the players playing ability. Test matches are played between national representative teams. Which has been given the test status determined and respected by the International Cricket Council (ICC).
Teams with Test Status and Debut Dates
| Team | Test Debut Date |
|---|---|
| Australia | 15 March 1877 |
| England | 15 March 1877 |
| South Africa | 12 March 1889 |
| West Indies | 23 June 1928 |
| New Zealand | 10 January 1930 |
| India | 25 June 1932 |
| Pakistan | 16 October 1952 |
| Sri Lanka | 17 February 1982 |
| Zimbabwe | 18 October 1992 |
| Bangladesh | 10 November 2000 |
| Ireland | 11 May 2018 |
| Afghanistan | 14 June 2018 |
Types of test matches:-
There are two types of test matches.
- Day Test Match: A day test match is played with a red ball.
- Day/Night Test Match: The day/night test match is played with pink balls.
In a test match, all the players as well as the umpire wear white clothes. 90 overs are bowled in a day in a test match. According to the rule, the new ball is available after 80 overs. Four innings are played in a test match. Which is divided into three parts: 1st session, 2nd session, and 3rd session. Each session is 30 overs, and after the first session is completed, there is lunch, and then after the next 30 overs, there is a tea break.
There are three reviews for a team in a test match. Free hit is not given on no ball in the test match. In a test match, stumps occur after 90 overs. Stumps mean the end of that day’s play in a test match.
How is a test match drawn?
A drawn match in a test match occurs when it is the last day of the match (5th day), and the team that is batting on the 5th day does not allow its team to be all out till the end of the game. No matter what the lead of the opposing team is.
WTC Winners & Runners List (2019-2023):-
| Year | Winner | Won By | Runner Up | Venue |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2021-23 | Australia | 209 Runs | India | Kennington Oval, London |
| 2019-21 | New Zealand | 8 Wickets | India | Southampton |
WTC Winners List with Captain, Man of the Match
| Year | Winner | Captain | Man Of The Match |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2021-23 | Australia | Pat Cummins | Travis Head |
| 2019-21 | New Zealand | Kane Williamson | Kyle Jamieson |
One-Day International:-
One Day International is a style of cricket in which 50 overs per team are played between two national cricket teams. This match is also called LOI (Limited Overs International). It was introduced in the 1980s, and 60 overs are bowled on a side. The dress code was the same as in Test cricket. Over the years, the rules of this format also changed drastically, and it was reduced to 50 a side and colored uniforms. The red ball was replaced with a white ball.
- At present, one-day international cricket is played between two teams with 11 players per team. The captain who wins the toss can choose either batting or bowling.
- In the early days of ODI cricket, the number of overs per team was generally 60, but this has now been uniformly limited to 50 overs. Each bowler can bowl a maximum of 10 overs. Only 11 players in a team can play a match.
- If a player gets injured during the match, another player can be fielded in his place. According to the new rules of the ICC, if the injured player has a head injury, only in this case can another player be made to bat or bowl. In case of any other injury, the second player can only field.
- If both teams score the same number of runs in 50 overs of their innings, it is called a “tied” match. After this, both teams are given one more over, which is called “Super Over,” where the team scoring more runs is the winner.
- If the scores of both teams are equal even in the super-over, then the super-over is conducted once again.
- At present, there are a total of three powerplays in one-day international cricket. The first powerplay will be from overs 1 to 10, the second from overs 11 to 40, and the final powerplay will be from overs 41 to 50.
Cricket World Cup Winners List (ODI) (1975-2023):-
| Year | Host | Winner | Winners Score | Runner-up | Runner-up Score | Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1975 | England | West Indies | 291–8 | Australia | 274 | West Indies won by 17 runs |
| 1979 | England | West Indies | 286–9 | England | 194 | West Indies won by 92 runs |
| 1983 | England | India | 183 | West Indies | 140 | India won by 43 runs |
| 1987 | India and Pakistan | Australia | 253–5 | England | 246–8 | Australia won by 7 runs |
| 1992 | Australia & New Zealand | Pakistan | 249–6 | England | 227 | Pakistan won by 22 runs |
| 1996 | Pakistan and India | Sri Lanka | 245–3 | Australia | 241 | Sri Lanka won by 7 wickets |
| 1999 | England | Australia | 133–2 | Pakistan | 132 | Australia won by 8 wickets |
| 2003 | South Africa | Australia | 359–2 | India | 234 | Australia won by 125 runs |
| 2007 | West Indies | Australia | 281–4 | Sri Lanka | 215–8 | Australia won by 53 runs |
| 2011 | India and Bangladesh | India | 277–4 | Sri Lanka | 274–6 | India won by 6 wickets |
| 2015 | Australia & New Zealand | Australia | 186–3 | New Zealand | 183 | Australia won by 7 wickets |
| 2019 | England and Wales | England | 241 | New Zealand | 241–8 | The match tied after regular play and a super over; England won on a boundary count |
| 2023 | India | Australia | 241-4 | India | 240 | Australia has lifted the World Cup trophy by defeating India with a convincing 6-wicket margin. |
Cricket World Cup Names & Captains – 1975 to 2023:-
| Year | Winner | Captain | World Cup Names |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1975 | West Indies | Clive Lloyd | Prudential World Cup |
| 1979 | West Indies | Clive Lloyd | Prudential World Cup |
| 1983 | India | Kapil Dev | Prudential World Cup |
| 1987 | Australia | Allan Border | Reliance World Cup |
| 1992 | Pakistan | Imran Khan | Benson & Hedges World Cup |
| 1996 | Sri Lanka | Arjuna Ranatunga | Wills World Cup |
| 1999 | Australia | Steve Waugh | ICC World Cup |
| 2003 | Australia | Ricky Ponting | ICC World Cup |
| 2007 | Australia | Ricky Ponting | ICC World Cup |
| 2011 | India | MS Dhoni | ICC Cricket World Cup |
| 2015 | Australia | Michael Clarke | ICC Cricket World Cup |
| 2019 | England | Eoin Morgan | ICC Cricket World Cup |
| 2023 | Australia | Pat Cummins | ICC Cricket World Cup |
Certainly! Below is an HTML table with CSS styling for the provided Women’s ODI Cricket World Cup winners from 1973 to 2022, organized in chronological order.
Women’s ODI Cricket World Cup Winners (1973-2022):-
| Year | Winner | Runners-up | Host |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1973 | England | Australia | England |
| 1978 | Australia | England | India |
| 1982 | Australia | England | New Zealand |
| 1988 | Australia | England | Australia |
| 1993 | England | New Zealand | England |
| 1997 | Australia | New Zealand | India |
| 2000 | New Zealand | Australia | New Zealand |
| 2005 | Australia | India | South Africa |
| 2009 | England | New Zealand | Australia |
| 2013 | Australia | West Indies | India |
| 2017 | England | India | England |
| 2022 | Australia | England | New Zealand |
T20 International:-
A form of cricket played between two members of the International Cricket Council (ICC), in which each team faces twenty overs.
This is the latest and most successful format of cricket. It attracted a large number of spectators to the ground. Cricket became a widespread sport in this format and was rapidly adopted by new countries such as the United States, Malaysia, Canada, and the Netherlands. It originated in the Caribbean Islands and the West Indies. Each team gets a chance to play 20 overs from a side. Since this is the shortest format of the game, it is played under floodlights. The first men’s T20 international match in history was played between Australia and New Zealand on February 17, 2005.
T20 World Cup Winners List (2007-2022):-
| Year | Winner | Runner-Up | Player of the Series | Top Run Scorer | Highest Wicket Taker | Host |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2007 | India | Pakistan | Shahid Afridi | Matthew Hayden | Umar Gul | South Africa |
| 2009 | Pakistan | Sri Lanka | Tillakaratne Dilshan | Tillakaratne Dilshan | Umar Gul | England |
| 2010 | England | Australia | Kevin Pietersen | Mahela Jayawardene | Dirk Nannes | West Indies |
| 2012 | West Indies | Sri Lanka | Shane Watson | Shane Watson | Ajantha Mendis | Sri Lanka |
| 2014 | Sri Lanka | India | Virat Kohli | Virat Kohli | Ajantha Mendis | Bangladesh |
| 2016 | West Indies | England | Virat Kohli | Tamim Iqbal | Mustafizur Rahman | India |
| 2021 | Australia | New Zealand | Mitchell Marsh | Babar Azam | Adam Zampa | UAE/Oman |
| 2022 | England | Pakistan | Sam Curran | Virat Kohli | Wanindu Hasaranga | Australia |
T20 World Cup Winners by Country
| Country Name | No. of times Winner | Year |
|---|---|---|
| West Indies | 2 | 2012, 2016 |
| India | 1 | 2007 |
| Pakistan | 1 | 2009 |
| England | 2 | 2010, 2022 |
| Sri Lanka | 1 | 2014 |
| Australia | 1 | 2021 |
Cricket Field Dimensions:-
In the cricket field, the pitch is like a soul; many captains decide the strategy of the match according to the pitch, and batsmen and bowlers also always want the pitch to be as per the pitch so that it becomes easier for them to play. The game is probably played on a circular flat field with a pitch in the center. The length of the pitch is 24 yards and the width is 4 yards. A rope is placed around the field at a distance of 80 yards from the pitch. According to ICC rules, the minimum diameter of the cricket field is 137.16 meters, the lower boundary of the pitch is 59.50 meters, and the maximum length is 82.29 meters.
- The length of the cricket pitch is 20.12 meters the width is 3.05 meters, and the distance between the popping creases is 17.68 meters. it occurs. This length of the pitch is the distance from one stump to the other; it does not include the place where the wicketkeeper stands. If the distance from one stump to another is measured in steps, it is 26 steps, while the distance between one crease and the other is 23 steps.
- The width of the cricket pitch is 10 feet, which, if seen in meters, is 3.05 meters. Although the width of the cricket pitch is greater, only 10 feet of space is used during play.
- On a cricket pitch, the length of the bowling crease from the stump is 4 feet, which is 1.22 meters. A line of 4–4 feet is made on both the front and back sides of the stump.
- On a circular boundary, the minimum distance from the pitch to the boundary line is 64 meters, and the maximum distance is 82.29 meters.
-
For the women’s cricket team, the distance of both the straight boundary and the square boundary is equal; the distance of the boundary from the pitch is a minimum of 64 meters (210 feet) and a maximum of 82.29 meters (270 feet).
All Equipment For Cricket:-
Along with the rules of the game, ICC has also made some rules for cricket equipment. The bat, ball, gloves, pads, and all other equipment must meet the standards set by the governing body. It is not only the size of the equipment but also the logos used on the equipment that must conform to the standards set by the ICC. The equipment used for sports should be used as per the rules. As cricket is a game of bat and ball, the players are subjected to wearing protective gear to not get hurt. In this chapter, we will discuss all the important gear and equipment that the players. The list of cricket equipment with the permissible measures is given below:

Ball:- It is a spherical object made out of cork and covered with leather. Two pieces of leather are stitched around the cork ball. The ball’s color for test matches is red and white for ODI and T20 matches. The weight of the ball in cricket should be between 155.9 to 163 grams. Apart from weight, the circumference should be between 224 and 229 mm. There are different rules in ODI and Test cricket regarding change of ball.

These are worn on both hands for protection. So that Fingers and hands do not get hurt. The inside of the gloves should have finger space with cork tips for added protection The fielding team in the cricket field has a wicketkeeper, who does the keeping with gloves. Apart from the keeper, no other player has any type of gloves in his hands. Only the wicketkeeper has the right to catch the ball with gloves. The keeper glove doesn’t have specific measurements but should not be made of stretchable material. The glove has webbing between the thumb and the index finger.

Wicket Keeper/Batsman:- Pads are important protective equipment worn by both batsmen and wicket keepers in cricket. Made from a combination of cloth and leather, these pads work to shield the lower limbs. The front portion is reinforced with hard plastic or wooden sticks, providing strong protection against cricket balls. In contrast, the backside is made soft and spongy, providing a cushioning effect for better comfort on the feet. Keeper pads are slightly smaller than batsman pads, the intricate construction of these pads reflects a careful balance between protection and comfort, ensuring players can perform optimally with minimal risk of injury.

Stumps:- Stumps in cricket are elongated cylindrical structures, resembling spears, utilized as essential equipment on the field. One end of the stumps is pointed and inserted into the ground, ensuring they stand upright. These structures are a fundamental component of the game, serving as the target for bowlers aiming to dismiss batsmen and contributing to the overall setup of the playing field. Stumps play a pivotal role in defining the playing area, and their strategic placement is crucial in various aspects of the game, including dismissals and determining the legitimacy of deliveries.

Striker/Non-striker:- In cricket, the batsman facing the bowler is referred to as the striker, while the batsman at the opposite end is termed the non-striker. The striker is the one actively engaging with the bowler, attempting to score runs, while the non-striker assumes a supporting role, awaiting their turn to take the striking position. This dynamic defines the roles of the two batsmen at either end of the pitch during a cricket match.
Off-side/leg-side:- In cricket, the terms “off-side” and “leg-side” define two different parts of the playing field. For a right-handed batsman, the off-side refers to the right half of the pitch, in contrast, the leg-side encompasses the left half of the pitch, which lies behind the batsman when he takes strike. These terms are important for field placement, shot selection, and strategic bowling, providing a standardized way of planning strategies during a cricket match.
Run:- In cricket, “runs” are the basic unit of scoring. This occurs when the batsman facing the bowler successfully hits the ball and travels the distance between the stumps and the non-striker. Runs are generally scored in increments of one, two, or three, indicating the number of runs the batsman completes between the wickets. This is the basic scoring unit required to accumulate a team’s total score.
Four:- In cricket, “four” refers to the scoring result when the batsman hits the ball, causing it to cross the boundary line while rolling on the ground. This feat is usually known as hitting a four, and results in the batsman being credited with four runs.
Six:- In cricket, a “six” is scored when the batsman hits a shot that results in the ball falling beyond the boundary line without making contact with the ground inside the field of play. With this achievement, the batsman and the team get six runs.

Wide:- In cricket, “wide” is a term used for a ball that is bowled well out of the batsman’s reach. This occurs when the ball bowled is directed away from the batsman and goes far away from the return crease on the off-side at the batting end. Another scenario occurs when the ball bounces over the batsman’s head after being pitched, also known as a wide. And when such a delivery is declared, an extra run is awarded to the batting team.
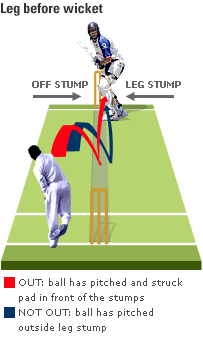
Out:- In cricket, a batsman is considered “out” when dismissed, creating an opportunity for the next player in the batting lineup. Dismissals can occur in a variety of ways, with common methods including being bowled, being caught out, being run out, being given out leg before wicket (LBW), or being stumped. These crucial moments turn the course of the game, as the batting team aims to score runs, while the fielding team attempts to dismiss all the opposing batsmen.
Bowled:- In cricket, the term “bowled” refers to a method of dismissal where the batsman fails to connect with the ball bowled, resulting in a hit into the back stump. The bowler’s primary objective is to bowl the ball in such a way that it tricks the batsman, and if successful, the stumps are uprooted, signaling the batsman’s departure from the crease. It is an important and efficient way of dismissing the batsman, showcasing the battle between the bowler’s technique and the batsman’s ability to defend or attack the ball.
Caught:- In cricket, the method of dismissal is “caught” when the batsman’s shot is caught by the fielder before the ball hits the ground. If the wicketkeeper takes the catch, it is specifically called a “caught-back”. This method of dismissal reflects the success of the fielding team and the bowler’s ability to inspire shots and is one of the important methods of dismissing a batsman during a cricket match.
Run-out:- Run-out is a method of dismissal in cricket, where a batsman is declared out if the fielding side successfully disrupts the stumps with the ball while the batsman is not within the crease. This happens when the batsman tries to take a run or is out of his crease after playing a shot.

Spin Bowling:- Spin bowling is a special technique in cricket where the bowler, standing a short distance from the stumps, uses his wrist or fingers to take the batsman’s wicket upon releasing the ball. The key characteristic of spin bowling is the ability of the ball to spin after being pitched. There are two main varieties of spin bowling: off-break and leg-break. In an off-break, the ball swings away from the right-handed batsman’s off-side, while in a leg-break the ball swings inside the batsman. Spin bowlers play a strategic role in exploiting pitch conditions, forcing batsmen to make mistakes, and contributing to the overall dynamics of the game.
Fast Bowling:- Fast bowling is a dynamic and high-velocity style of delivering the cricket ball to the batsman. Fast bowlers bowl long runs from the stumps to generate significant pace and bounce. Varieties of fast bowling include slow-medium, medium-fast, and fast, each characterized by different levels of pace and pace in the air or off the pitch. Fast bowlers play an important role in troubling the batsmen, creating momentum, and providing an aggressive dimension to the team’s bowling attack. Pace, aggression, and the ability to extract bounce make fast bowling a strong and effective aspect of cricket.
Extra Runs:- Extra runs in cricket refer to runs scored by the batting team without the batsman hitting the ball with his bat. These extra runs are awarded by the fielding team due to various violations such as wides and no-balls. A wide occurs when the bowler bowls a ball that is too far from the batsman’s reach, and a no-ball involves a breach of various rules by the bowler.
Innings:- An innings in cricket is a complete session of batting and bowling. It ends either when the batting team’s innings are completed by being all out or when the fielding team has bowled the allowed number of overs. During an innings, the batting team attempts to score as many runs as possible, while the fielding team aims to dismiss their opponents and prevent runs.